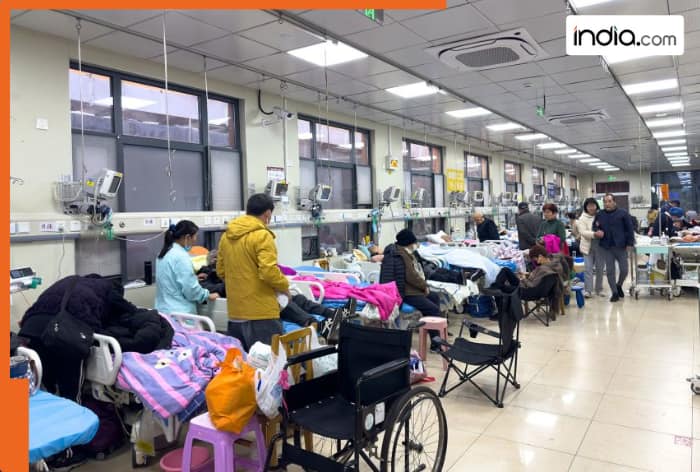
The United States prepares for a challenging flu season as the fast-spreading subclade K variant raises health concerns across the country.

What is the driving concern this year?
The reason for the worry is a mutated influenza strain known as “subclade K,” a variant of the influenza A (H3N2) virus that has been spreading rapidly in multiple countries. Genetic surveillance data show that subclade K now makes up the majority of H3N2 samples identified in the US so far this season, suggesting that it could dominate flu activity as the season continues. Normally, influenza viruses that circulate each year vary slightly from one season to the next, but subclade K has developed multiple genetic changes compared with previous versions. These changes help it spread more effectively and may make it less similar to the strain targeted by this year’s vaccine.
Why is it a serious concern?
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicate that subclade K now accounts for a significant portion of early influenza cases in the United States, despite overall flu activity still being in its early stages. Experts point out that influenza viruses constantly evolve, and changes like those seen in subclade K are a natural part of how the virus adapts and circulates globally. But when mutations occur after the flu vaccine composition is selected, there can be a mismatch that slightly reduces vaccine effectiveness.Source link













Leave a Reply